Do you know what leads to a reduction in your Home Loan rates? Or What factor influences the Bank deposit Rates?
Besides the Cost of funds and Liquidity Positions of the banks, RBI policies play a major role in these decisions. Though RBI doesn’t control these rates directly, its policies have a big influence on the bank interest rates.
The Major Objectives of RBI while formulating Monetary Policy are to control Money supply and Rate of interest in the economy to stimulate the growth. However, along with growth it also has to take care of the price stability, as commonly known as Inflation.
For High growth, the economy prefers lower interest rate and easy availability of credit, but high money supply leads to high Inflation which in turn has many side effects.
This management is not an easy job as lot many other factors like international Interest rates, Political actions, Currency fluctuations, the balance of payments, Government borrowing program, etc. need to be considered while devising the Monetary policy.
That’s why unlike Fiscal Policy (Budget), Monetary Policy gets reviewed every Financial Quarter, while a broad policy gets announced every year in April.
There are majorly 4 tools which RBI uses in the monetary policy which I have tried to simplify in the Infographics below.
Through these tools, RBI manages the money flow in the economic system and thus creates a balance between Inflation and Growth.
There are some more tools like OMO (Open Market Operations), MSF (Marginal Standing facility) and Bank rate. But since CRR, SLR, REPO rate and Reverse Repo are reviewed every quarter so these carries more importance in any Monetary Policy
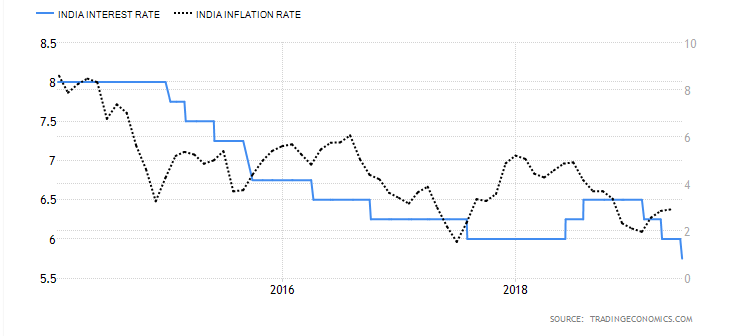
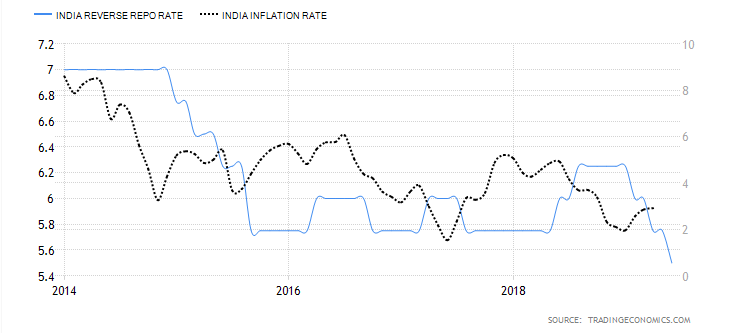
I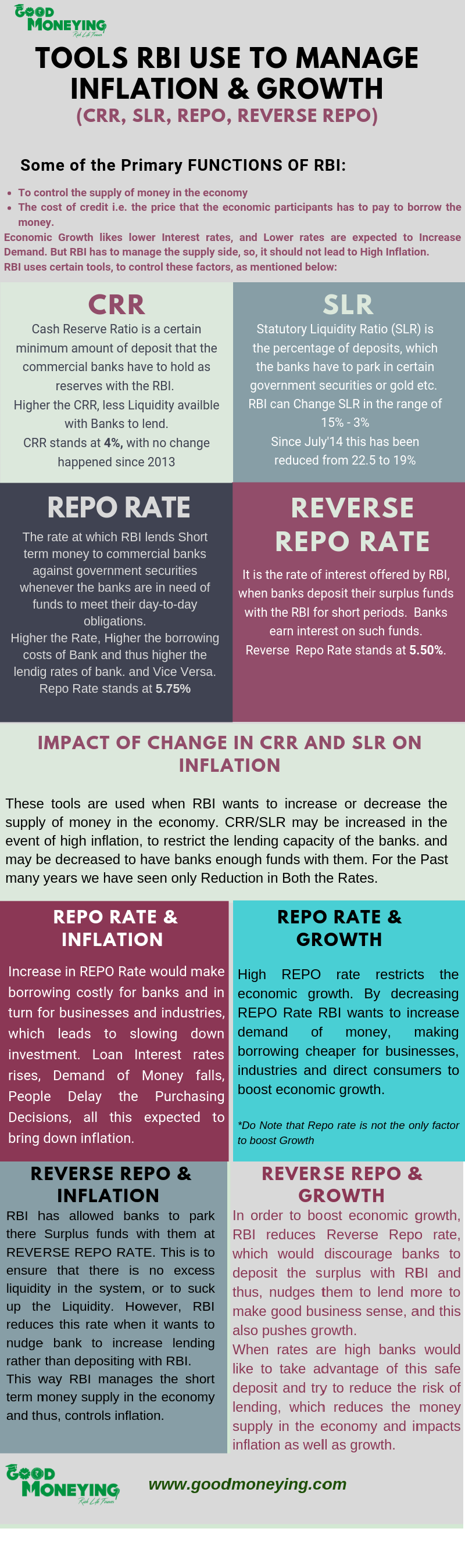 Impact of change in REPO and Reverse Repo Rate on Inflation
Impact of change in REPO and Reverse Repo Rate on Inflation
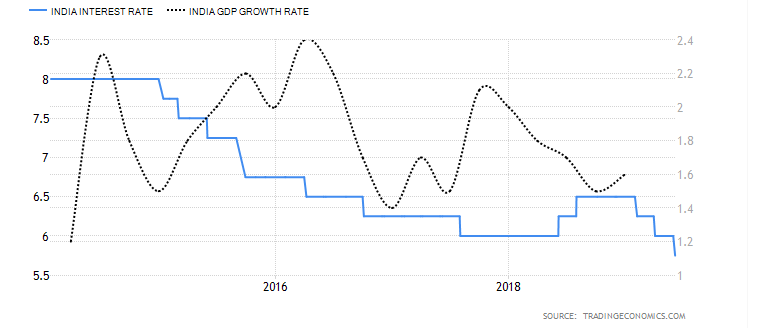
Impact of change in REPO and Reverse Repo Rate on GDP Growth
Conclusion:
CRR (Cash Reserve Ratio) and SLR (Statutory Liquidity Ratio) is meant to manage the Medium to the Long term Money supply, and thus impact the availability of the funds with banks. Whereas Reverse Repo Impact the short end of the money supply.
Repo rate is the Interest rate through which RBI manages the demand side of Money. In totality, all these among some others manage the Inflation and Growth in the Economy.
However, It is important to note that banks do not Pass the Lower rates benefit or Burden of High rates immediately to the customers after RBI announce any change. They have to look at the cost of the funds and Liquidity Position before making any decision.
That is why now the Regulator is coming with a rule where banks immediately have to act upon the deposit and lending rates based on decisions announced in the monetary policy, so to impact the inflation and Growth faster.