Fixed maturity plans or as popularly known as FMP comes under debt mutual fund schemes, but with a lock-in period or you may say with a Fixed maturity date.
The Product is structured in such a way as the maturity of the scheme coincides with the securities bought under the scheme and thus one may expect a fixed return from it.
An investor may have a clear understanding of the kind of returns he may expect looking at the portfolio of the scheme. And thus, fixed maturity plans are very much comparable to bank fixed deposit in terms of fixed returns.
FMP comes with an added advantage of being a Tax efficient instrument, being a Debt Mutual fund.
In this article, I am going to explain what FMPs are, how it works and how are fixed maturity plans a tax-efficient product as compared to traditional instrument like bank Fixed deposits?
What is a Fixed Maturity Plan (FMP)?
One thing that a Debt investor expect from his investment is Safety. Which is why they prefer Bank Fixed deposits, PPF, Bonds and sometimes Debt Mutual funds.
Unlike Bank deposits or Small saving schemes, Debt mutual funds are not a Fixed Return Instruments. The value of the scheme gets impacted by the movement in the interest rates.
If the market rates are moving higher than the value of bonds in which debt mutual funds have invested will go down and thus directly impact the scheme returns. The opposite is also true when the Interest rates are moving downwards that will increase the bond prices and thus NAV of the Debt mutual funds.
In Short, the Debt mutual funds’ returns are a factor of Bond prices which further depends on the market interest rate scenario. Thus, all open-ended debt funds get impacted by the interest movements, which makes it a volatile product in volatile interest scenario and may not be liked by the investors invested in for a fixed return.
Fixed maturity plans as the name says are those debt mutual funds which are close-ended and have a specific lock-in period. This product matures along with the debt securities it has in its portfolio and thus be able to provide investors with Fixed return. Whatever be the Interest rate scenario, FMPs are structured to offer a Fixed return to the investor.
The Portfolio constituents help you gauge the kind of rate you may expect from the product, as Mutual fund companies are not allowed to disclose the tentative rates which may be generated from it.
(Also Read: Perpetual Bonds in India)
In the Rising interest rate scenario or you may say in the volatile scenario, conservative investors looking for a fixed return kind of product may consider FMPs. Not only because of fixed returns but also because of tax efficiency it offers.
Fixed Maturity Plans (FMPs) – Tax Calculation
Being a debt mutual fund, the Tax calculation of FMPs are similar to that of other debt funds i.e. 20% after Indexation. As I am specifically referring to the FMPs with 3+ years of time horizon so I have only mentioned of Long-term capital gain tax.
However, FMPs do come with shorter time frame but in that case, the gains earned will be added in the total income of the investor and taxed as per income tax slabs and thus loses its tax efficient feature.
Fixed Maturity Plans are very well compared with Bank Fixed deposits due to its fixed return and maturity feature. But are well placed when comes to taxation.
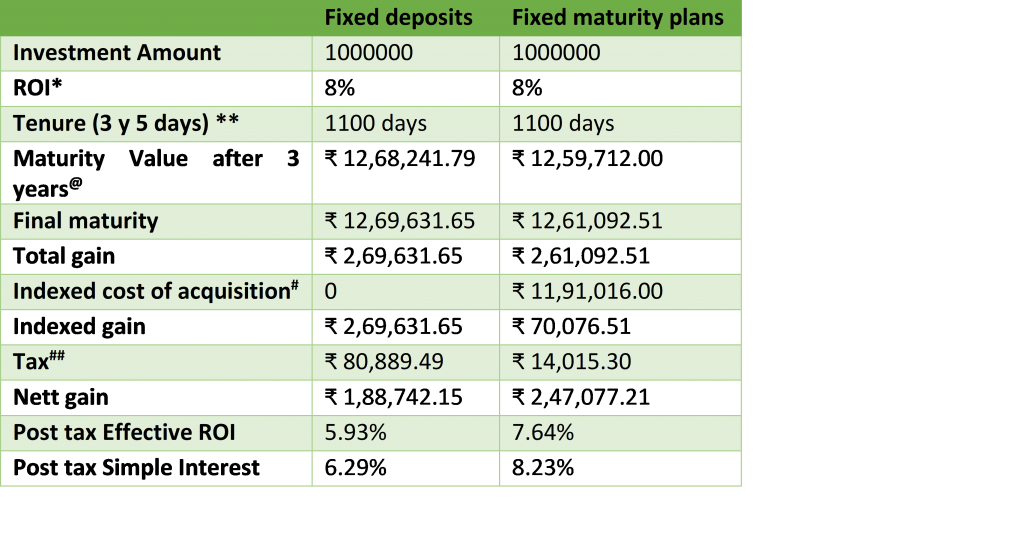
Below are the tentative calculations which will help you better understand the taxability of the FMPs
*Generally, the ROI in FMP is always higher than Bank FDs due to nature of the risk involved and also lower expenses vis a vis bank product.
**To cross over complete 3 years and come under LTCG taxation FMPs, comes with some 3y plus kind of tenure.
@FDs are Quarterly compounded so the Maturity value is higher than FMPs
#To Calculate Indexed cost of Acquisition, Inflation @ 6% YOY has been assumed. For actual calculation, you have to refer CII numbers (Read: How to calculate Indexed cost of acquisition)
##Tax in case of FD has been calculated at the highest slab of 30% without accounting for any Cess or Surcharges. And in case of FMP, the Tax rate is at 20%
You can very well see from the above table how FMPs have upper hand as compared to bank fixed deposits in generating Post-tax returns.
Fixed Maturity plans – Disadvantages
One should be aware of the restrictions or disadvantages also while deciding onto invest in any product. Where FMPs are attractive from returns and Taxation point of view there it has some associated risks also. (Also Read: Types of Risks in Investments)
Below are some of them:
- Liquidity Risk:
Unlike bank deposits, FMPs cannot be redeemed in between the tenure. Though these products are listed on Stock exchanges where one may sell at the prevailing rates, but for that, you have to have a buyer available. Being not so popular instrument demand of FMPs in the stock market is hardly anything.
- Credit Risk:
Besides Liquidity risk, FMPs are prone to Credit/default risk too. As the Fund manager has bought securities or you may say lend to different corporates having a varied credit rating, so default in repaying the money by any corporate will impact the expected return of the overall fund.
Though this risk can be managed by investing in FMP with 100% AAA (Highest Security) papers still you can never nullify this risk. This may be one of the reasons corporate bonds tend to offer higher rates than Bank fixed deposits. (Also Read: FD interest rates are rising in 2022- looking attractive again?)
- Being a fixed maturity, close-ended and fixed return instrument, the 3 years lock-in may result in loss of the opportunity to earn more in falling interest scenario. (Read: How to select debt funds in volatile interest scenario)
Conclusion:
FMPs are no doubt a better-placed tax efficient fixed return instrument but investing in it or not depends on your understanding and acceptability of the risks, as well as your requirement of funds.
Risks are there in every financial instrument, it is there in bank fixed deposits too, so it has to be a calculated call while making an investment decision.
If not FMP then the Short-term debt mutual funds may suit the short to medium-term investment requirement, with the open-ended feature.
Also Check: What are Target Maturity Funds and how are these different from Fixed Maturity Plans?